© 2023 by SacSpine. All rights reserved.
- 3415 American River Dr A, Sacramento, CA 95864
- Tel: (916) 648-0144
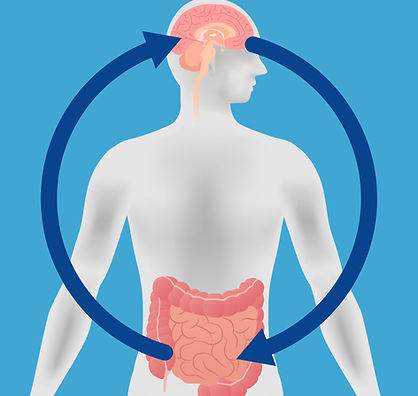
According to the National Institute of Health (NIH), The gut-brain axis (GBA) consists of bidirectional communication between the central and the enteric nervous system, linking emotional and cognitive centers of the brain with peripheral intestinal functions. Recent advances in research have described the importance of gut microbiota in influencing these interactions.
New research has shown that gut health has a direct impact on brain function. For example, studies have show that fasting can have a positive effect on the brain and overall health by:
Starving Microbes
Resting the Liver
Resting Pancreas
Resting GI Tract
Resetting Sensory Mechanisms
Gut health has been shown to have a role in brain related disorders such as Parkinson’s Disease (Lewy Body dementia) and diseases of the Enteric Nervous System. It has also been shown to affect emotional health, pain sensitivity and social interaction.
Gut health and immunity are closely linked. Most of the body’s immune cells reside around the gut. The gut, also known as the gastrointestinal tract, is home to trillions of microorganisms collectively known as the gut microbiota. These microorganisms play a crucial role in supporting the immune system and protecting the body against pathogens.
Research has shown that a diverse and balanced gut microbiota is important for maintaining a healthy immune system. The gut microbiota helps to regulate the immune response by producing immune-modulating substances such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which help to prevent inflammation and promote the growth of beneficial bacteria.
In addition, the gut is a site of immune system activity. The lining of the gut contains immune cells that help to recognize and destroy harmful bacteria and viruses that may enter the body through the gut.
Furthermore, the gut microbiota is also involved in the production of antibodies, which are proteins that help the immune system to recognize and fight specific pathogens.
Therefore, maintaining good gut health is important for maintaining a healthy immune system. Eating a balanced diet that is rich in fiber, prebiotics, and probiotics can help to support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. Additionally, reducing stress levels, getting regular exercise, and getting enough sleep can also help to maintain a healthy gut and support a healthy immune system.
© 2023 by SacSpine. All rights reserved.